Virtual FAS by Learning-Based Imaginary Antennas
Published in IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2024
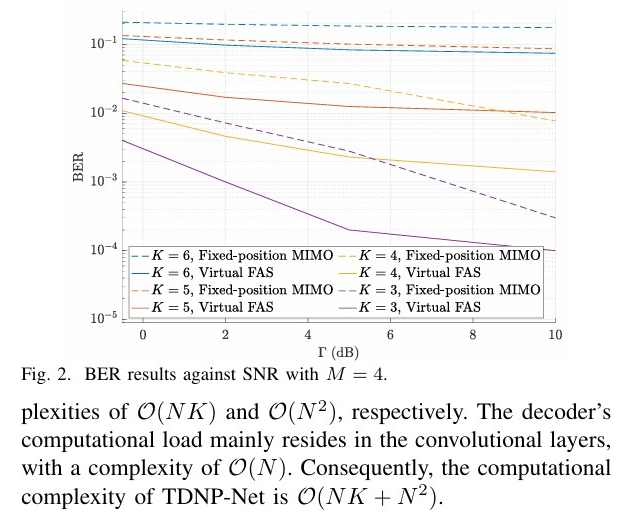
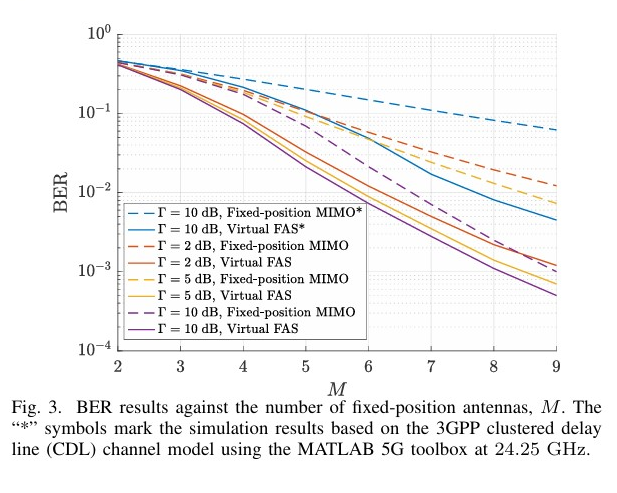
Abstract: Fluid antenna system (FAS) represents a new tech nology able to flexibly and instantaneously change the antenna position for optimizing wireless communication performance. The high-resolution adjustment of the antenna position is what makes FAS powerful in taking full advantage of the fading variation in space. To obtain the benefits of FAS but without the complication of implementing FAS, this letter considers a mobile receiver with several fixed-position antennas and employs a transformer-based signal prediction network to deduce the received signals at other positions. This is possible since the received signals are correlated in space. The outcome is an increased dimension multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) receiver which can be interpreted as a virtual FAS with imaginary antennas. We evaluate the proposed system in multiuser channels and adopt regularized zeroforcing (RZF) in the virtual FAS to deal with the interference. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed virtual FAS outperforms significantly the original fixed-position MIMO system. Index Terms: Antenna array, fluid antenna system, imaginary antennas, machine learning, multiuser communications.
Recommended citation: Wong, Kai-Kit, et al. "Virtual FAS by learning-based imaginary antennas." IEEE Wireless Communications Letters (2024).
Download Paper
